Sustainable water treatment for the safe operation of boiler houses
Sustainable water treatment in boiler houses done right
Installation of sustainable feedwater treatment in boiler houses.
The objective is to prevent water-side deposits in the boiler in order to increase efficiency, extend service life and save costs in boiler feedwater treatment systems.
The background is that water hardness and associated deposits of lime, sulfates, silicates on the heat exchange surfaces in the feed water lead to high energy loss and increased costs for decalcification, as well as for the repair of numerous other damages to the boiler system and its components.
In the worst case, inadequate water treatment can shut down the entire production of an entire company due to failure of the boiler system.

What are the risks of water treatment in boiler houses?
Initial situation / as-is analysis
Boiler feed water is water that is stored in a feed water tank and continuously fed to a steam generator. Particularly large quantities of feedwater are used, for example, for steam generation in power plants in order to control process engineering processes or the drive of steam turbines/steam engines with the generated steam.
This requires specially treated feed water, which must meet certain requirements to avoid reduced performance and damage to the plant.
The challenges in the treatment of boiler feed water lie in
- pH values that are too low or too high
- gases dissolved in the water such as oxygen and carbon dioxide
- too much silicate
- foaming boiler water
- contaminated condensate
- soda splitting
- inefficient / wrong chemicals
- boiler corrosion
- insufficient technical treatment of raw water
- insufficient feed water treatment
This leads to the formation of deposits on the water side, such as corrosion, scale, lime, sulfates, silicates and calcium phosphates, which can lead to poorer heat transfer and the resulting thermal stress cracks. This leads to poorer efficiency of the plant. In addition to the decreasing efficiency of the plant, costs for maintenance and servicing increase.
Targets in the feed water treatment in the boiler house
Goals / Business requirements
The aim of water treatment is to achieve many years of trouble-free operation of boiler feed water systems through optimum feed and boiler water quality.
Without exception, water from natural sources does not meet the quality requirements, depending on the design and operation of the steam boiler, which are enshrined in European standards such as EN 12952-12 and EN 12953-10, as well as in other regulations such as VGB and VdTÜV.
The aim is to achieve the quality of the feed water, make-up water and boiler water in accordance with standards and regulations with the aid of various water treatment processes.
The focus is on increasing the efficiency of the boiler plant through smooth operation and reducing repair and maintenance costs by extending the service life of pipe systems and boilers.
In addition, the installation of a sustainable water treatment system is intended to optimize energy costs by preventing deposits in the boiler and, consequently, heat transfer.
In summary, the following advantages result from the above target description when installing a sustainable water treatment system:
- Prevention of scale formation
- Prevention of sludged pipelines, pumps, condensers and heat exchangers
- Rust protection in the entire plant
- Improved heat transfer
and due to these factors
- Maintaining the value of the entire boiler feedwater system
Investigated solution variants
The inspection of boiler feedwater systems, the analysis of make-up water, feedwater and boiler water, and the analysis of the technical and chemical treatment of the water result in different solution variants. These range from the smallest adjustment screws in raw water treatment to the establishment of continuous control systems for parameters such as water hardness, carbonate hardness and conductivity.
The solution variants depend on the existing system. However, a combination of technical and chemical water treatment is always necessary to increase efficiency and operational safety.
For this purpose, it is worth taking a look at the central components of a steam generation plant:
- Boiler water treatment
- Steam generators, steam boilers
- Steam lines
- Consumers
- Condensate
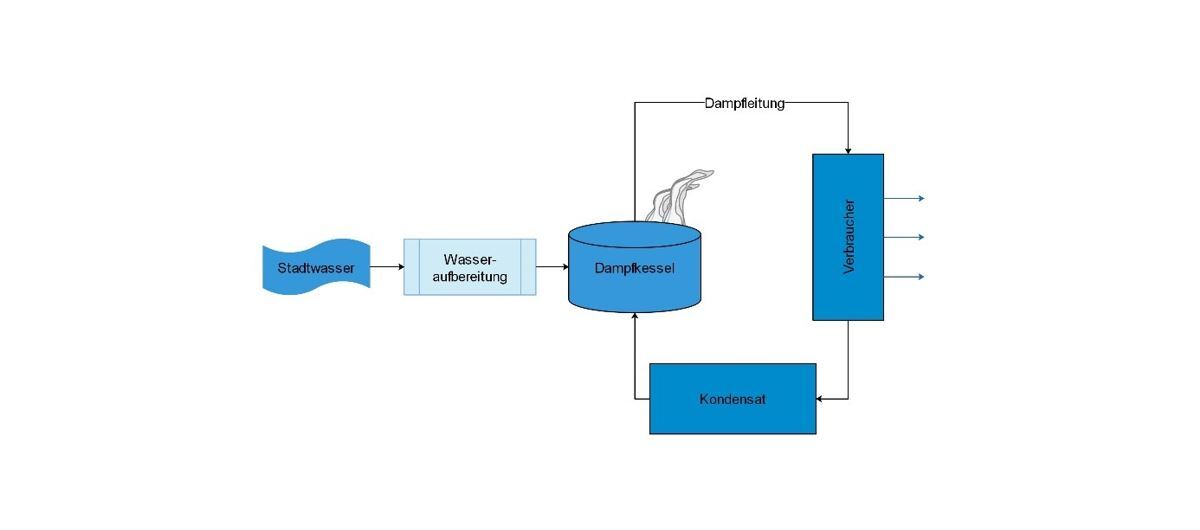
In every steam plant, there are thus at least 2 points where the aggregate state of the working medium water changes:
- The applied heat (heat of evaporation) produces water vapor from water
- The water vapor releases its heat (heat of condensation) and water (condensate) is formed again
Accordingly, the boiler feed water treatment is divided into 2 steps.
Step 1 (First treatment of the boiler feed water):
- Prefiltration: removal of iron and manganese by filtration
- Softening: removal of hardness minerals calcium and magnesium ions
- Desalination: removal of all dissolved salts by reverse osmosis / ion exchanger
- Degassing: removal of dissolved, corrosive gases CO2 and O2 by thermal degassing
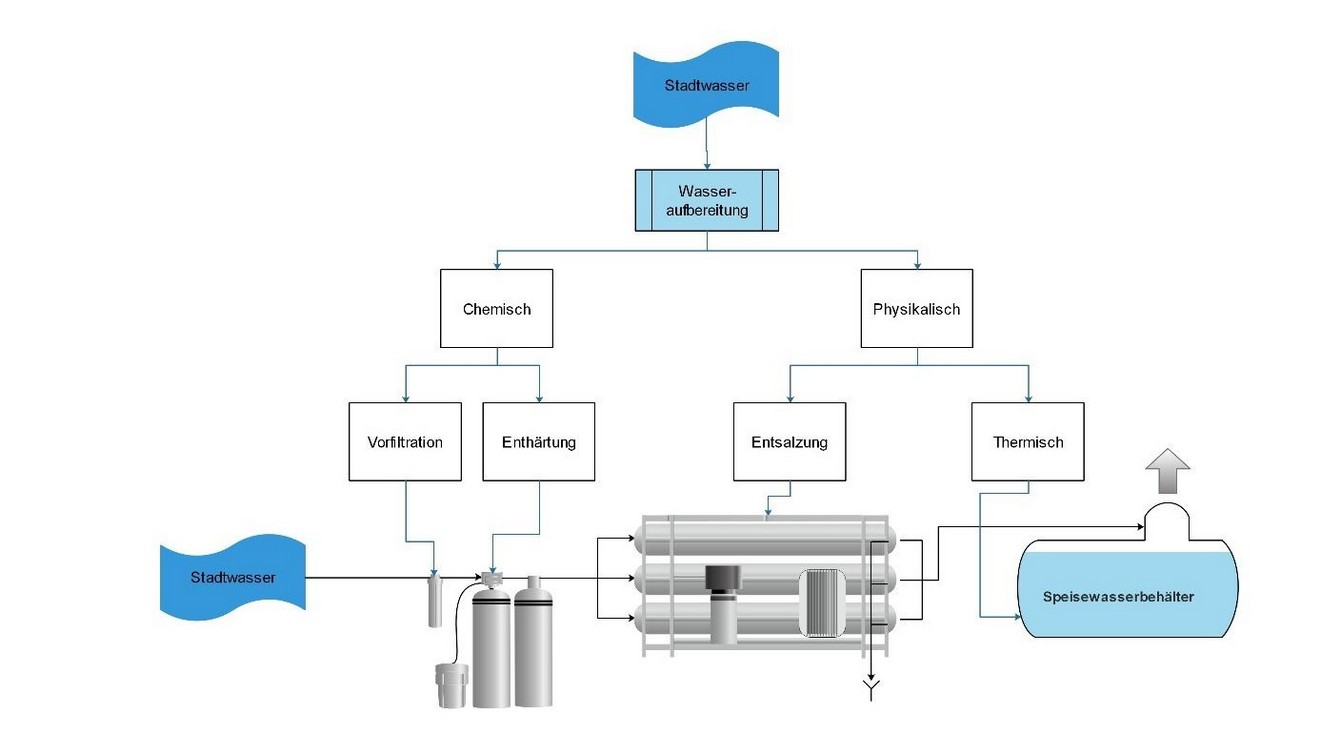
Water treatment in boiler houses, second step
Thermal full degassing can remove the dissolved gases. This prevents pitting in the steam boiler.
Step 2 (Second treatment after physical preparation):
- Oxygen binder: e.g. sodium sulfite (Na2SO3)
- Boilermaking agents: e.g. trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4)
- Corrosion inhibitors (film forming amines): e.g. Duomeen O, Naylamul S11
- Alkalizing (ph-correction): e.g. Diethlyaminoethanol (DEHA)
Subsequently, the chemically and thermally treated feed water is checked by sampling and, if necessary, corrected by dosing chemicals.
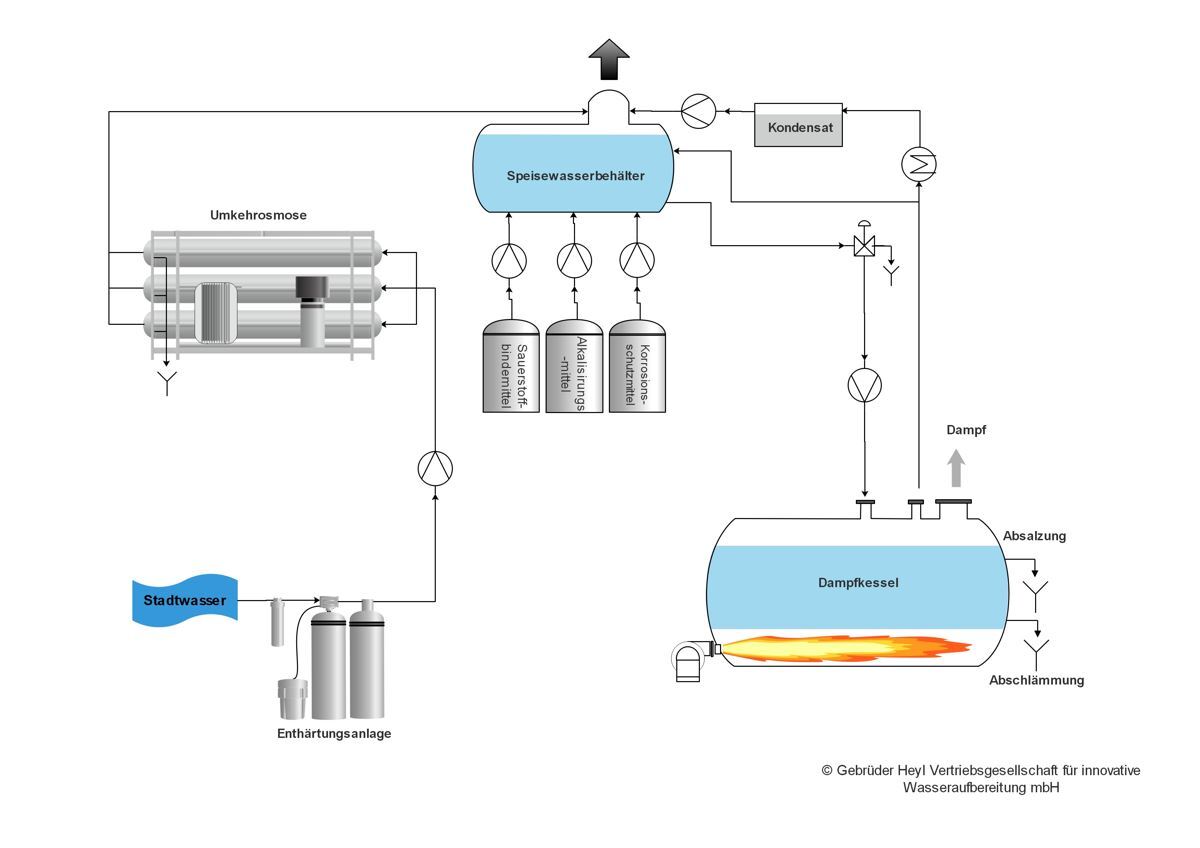
After these steps, the boiler feed water is treated and the treatment system is installed.
The following monitoring and measuring devices are suitable for the required continuous process control (see also schematic diagram):
- Controls for the softening plant
- Controls for the reverse osmosis plant
- Devices for monitoring the residual hardness in the make-up water
- Conductivity measuring devices
- pH-value measuring devices
- Devices for monitoring the sulfite concentration in the feed water
- Devices for monitoring ortho-phosphate or polymer
- Four-channel multiparameter transmitters for visualization
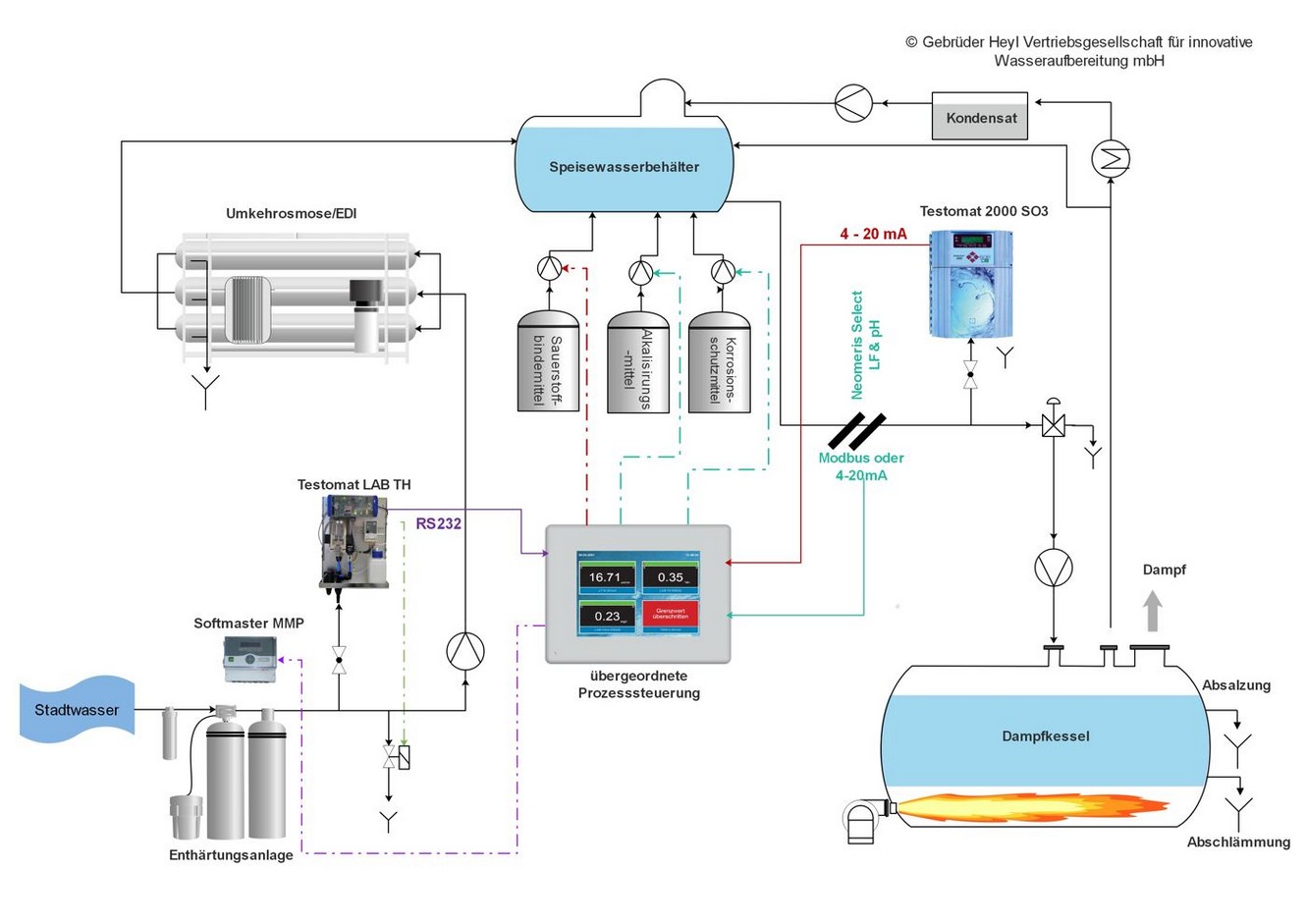
How exactly does the optimization of the boiler feedwater system succeed now?
With a professional calculation of the boiler water treatment, in which the feed water quality and the mode of operation play an important role, the right measures can be determined.
Based on the calculation, a selection of products for efficient technical and chemical treatment of water is made. Here, there are applications where a single product ensures smooth and long-lasting operation of the equipment. Often, however, a combination of different products makes sense.
This shows that there is no boiler feedwater treatment “par excellence”, since the quality and composition of boiler water, feedwater and make-up water vary greatly, and the different pressure levels of steam generators have to be taken into account.
For this reason, we offer our customers a comprehensive concept ranging from consulting and analysis of water parameters to the creation of an individual concept for water treatment in boiler feed water systems.
The solution variants are aligned to your cost optimization as well as benefit increase.
The selection of the water treatment process depends on the budget as well as on how much efficiency, safety and economy is to be achieved.
One-time costs:
- Consulting and planning costs
- Investment costs for measuring devices for monitoring water hardness, carbonate hardness and conductivity
Der ROI der Anlageninvestition wird in der Regel innerhalb des ersten Jahres erreicht.
Folgende Kostenpunkte werden durch eine nachhaltige Wasseraufbereitung optimiert:
Periodisch anfallende Kosten:
- Reduktion der Kosten für Chemikalien zur Aufbereitung des Kesselwassers, Speise- und Zusatzwassers
- Reduktion der Wartungs- und Instandhaltungskosten durch einmal jährliche Serviceeinsätze
Laufend anfallende Kosten:
- Energieeinsparung beim Betrieb der Anlagen durch optimierte Wärmeübertragung
- Steigerung von Umsätzen durch geringere Stillstandzeiten, weniger Produktionsausfälle und geringeren Wartungsaufwand
Furthermore, the investment does not primarily result in monetary benefits:
- Saving of working time in the departments, repair, maintenance and servicing
- Shorter process runtimes
- Ecologically sustainable water treatment
- Increased employee satisfaction due to smooth operating processes
Risk analysis
The costs of plant downtime are measured not only in terms of actual downtime, but also in terms of the time and costs involved in making the plant operational again. Furthermore, the extent to which higher-level processes and services have been impaired in the meantime by this disruption must be taken into account. Therefore, it is crucial that the performance of the entire system is maintained.
Professional monitoring of water treatment and the associated early detection of performance degradation can prevent damage and reduce downtime and lost revenue.
Recommendation, decision template
Analysis and evaluation of the existing boiler water treatment process including the creation of an individual concept for sustainable water treatment in boiler plants.
Based on the individual concept proposals, measuring and monitoring devices are installed at the water treatment plant, depending on the desired degree of target achievement in efficiency, safety and economy.
What are the effects of incorrect ph values?
Incorrect ph values lead to deposits on the water side and poorer heat transfer.
What can lead to a loss of production?
Deposits on the water side lead to poorer heat transfer and can promote stress cracks in the boiler. This reduces the efficiency of the system.
In individual cases, this can lead to total failure of the system.
What is the risk of unsafe water treatment?
Unsafe water treatment leads to energy losses, high maintenance and servicing costs.
In the worst case, production is lost due to plant shutdown.
Which measurement parameters are decisive?
Measuring and monitoring devices control water hardness, carbonate hardness and conductivity.
What happens due to deposits on the water side?
This results in scale formation, silted piping, pumps, condensers and heat exchangers, and rust throughout the system.